Enterprise Mobility & the Connected Worker Blog
Green Initiatives and Sustainability Practices are increasing in the World of Enterprise Mobility
Climate change is one of the most important issues affecting the future of all life around the globe. Growing advocacy movements to address the causes of man-made climate change and prepare society for a greener future have led leaders in both the public and private sectors promising to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable practices. Governments are enacting policies that encourage the reduction of their nation’s carbon footprints, while enterprises are adapting to these policies with more sustainable and cleaner business models. In the world of enterprise mobility, solution providers are taking action to “go green” while also reducing the footprints of their customers.
To start, many mobile device manufacturers have been utilizing recycled materials in the production of their devices. As more and more mobile devices are shipped for use each year, there is an opportunity to reuse plastics and materials from older devices in the new manufacturing process to counteract the increased risk of pollution from increased production. Dell Technologies has been a leader in this recycled practice for over 10 years, taking materials from e-waste and recycling them into new devices. Apple has also taken huge steps towards climate action. In 2018, the company began manufacturing its products with aluminum that had been produced through carbon-free smelting technology. This innovation was revolutionary, as the process for smelting aluminum had remained unchanged since 1886.
Innovation and investment in cleaning up the manufacturing process of mobile devices has been a gigantic step in the move towards a more sustainable future. Enterprise customers can, in turn, reduce their own footprints by choosing vendors that are using ‘green’ production methods. However, pollution occurs throughout the entire supply chain and efforts need to be made to reduce emissions at all stages and beyond. In May 2021, 5 of Europe’s leading mobile operators (Deutsche Telekom, Orange, Telefónica, Telia Company, and Vodafone) created an Eco Rating labelling scheme that scores the overall environmental performance of a mobile device across its entire lifecycle. The rating is based on 5 scores: durability; ‘repairability’; recyclability; climate efficiency; resource efficiency. So far, 16 mobile device suppliers, including Nokia, Motorola, Samsung, Huawei, and more have signed up to participate. This Eco Rating gives customers the newfound ability to assess the environmental impact of their mobile fleet procurements and empowers them to reduce their own footprint.
While cleaner production technology developments and transparency to empower customers for environmentally-friendly purchasing show the progress made by the mobile device ecosystem in addressing climate change, there is always more that can be done. Some of the largest mobile device vendors are creating initiatives to fund innovation and ‘green’ technologies. In 2016, Apple launched its Green Bond, which funds environmentally-focused projects across several categories: “Low Carbon” Design and Engineering; Energy Efficiency; Renewable Energy; Carbon Mitigation; Carbon Sequestration. In 2021 alone, Apple provided over $220 Million to 43 of these projects. Panasonic has followed suit, creating its Green Impact initiative at the beginning of 2022. This initiative has three main goals: to achieve net-zero carbon dioxide emissions across all operating companies by 2030; to reduce the CO2 emissions of customers through the use of Panasonic products; to contribute to the reduction of CO2 emissions by society through the expansion of Panasonic solutions that use clean energy or reduce energy consumption.
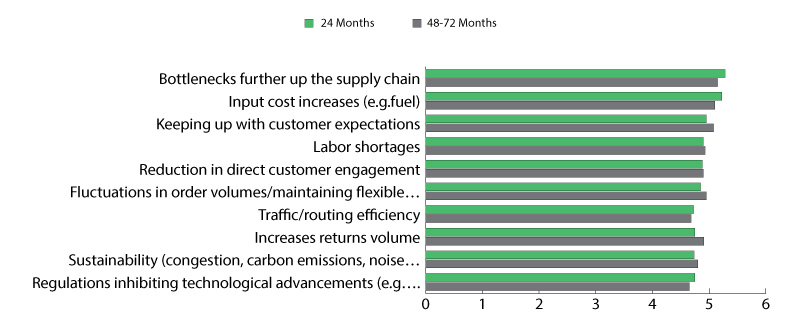
As advocacy to fight climate change continues to grow, we expect government policies and enterprise initiatives to follow with further green technology innovation and sustainable business model adaptation. Environmental impact has not traditionally been a major factor in purchasing decisions among enterprise, but soon it may be a complete differentiator. Exhibit 1 shows that retailers do not see sustainability as a significant challenge to last mile delivery operations over the next 2 years; however, in the next 4-6 years it will be more of a concern. In the near future, device manufacturers will look to integrate their solutions into environmental projects and research, while customers will seek mobile tools from providers with lower emissions.
Exhibit 1: Anticipated impact of challenges to last mile delivery operations in retail, next 24 months vs 48-72 months (MEAN: Likert scale 1 = least impactful; 7 = most impactful)